1. Connect your laptop to an IP phone.
2. Start Wireshark
3. Listen to traffic and wait until you capture a CDP package.
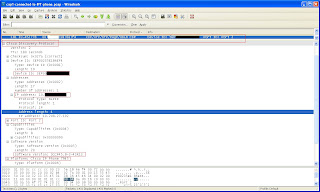
4. Connect to the http interface of the phone and review the VLAN number

5. Using voiphopper run the following command using the information discovered on the CDP packet and the phone HTTP interface.
./sudo voiphopper -i eth0 -v VLAN# -E DEVICE_NAME -P PORT_ID -C HOST -L DEVICICE_ID -S SOFTWARE_VERSION
It is really important that you know that when you do VLAN hopping you usually can bypass network restrictions that you will usually have connected to a user network, this can be really helpful in any kind of pentest and not only when testing VOIP.
This is a good link that explains the basics of VLAN hopping:
http://www.securityfocus.com/infocus/1892
4. Run nmap to identify the services that are available on your network. It is important that you also identify servers to which the telephones are reporting such as TFTP server.
5. When you identify the TFTP server a good way to learn more about the IP telephony infrastructure you can do the following: Using tftpbrute or a simple TFTP client try different file to download from the TFTP server.
./tftpbrute.pl IP_ADDRESS brutefile.txt 100
List of files that might work:
fsck.fd0a.log
fsck.fd1a.log
jar45sccp.8-3-3-17.sbn
Ringlist.xml
DEVICE_NAME.cnf.xml
term45.default.loads
Test that the TFTP server is well configured and that you cannot upload any random file to it. Please keep in mind whenever you are uploading files to the TFTP server that all IP phones will take this files as configuration files so you can really screw the hole VoIP infrastructure if you are not careful.
c4an.
No comments:
Post a Comment